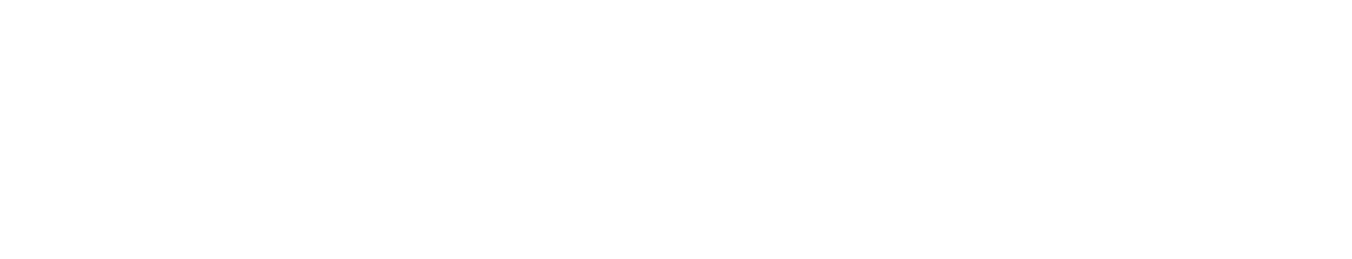
Hypothesized Steatosis–Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathway

In the absence of common hepatic insults, such as excess alcohol, accumulation of fat in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)) is associated with chronic inflammation, known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In some subpopulations, over time, NASH may progress either directly to hepatocellular carcinoma or indirectly through a cirrhosis state. ECM, extracellular matrix; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF, tumour necrosis factor. FROM: Adiposity and cancer risk: new mechanistic insights from epidemiology. Nature Reviews Cancer 15, 484–498 (2015). Andrew G. Renehan, Marcel Zwahlen & Matthias Egger“ (with permission).